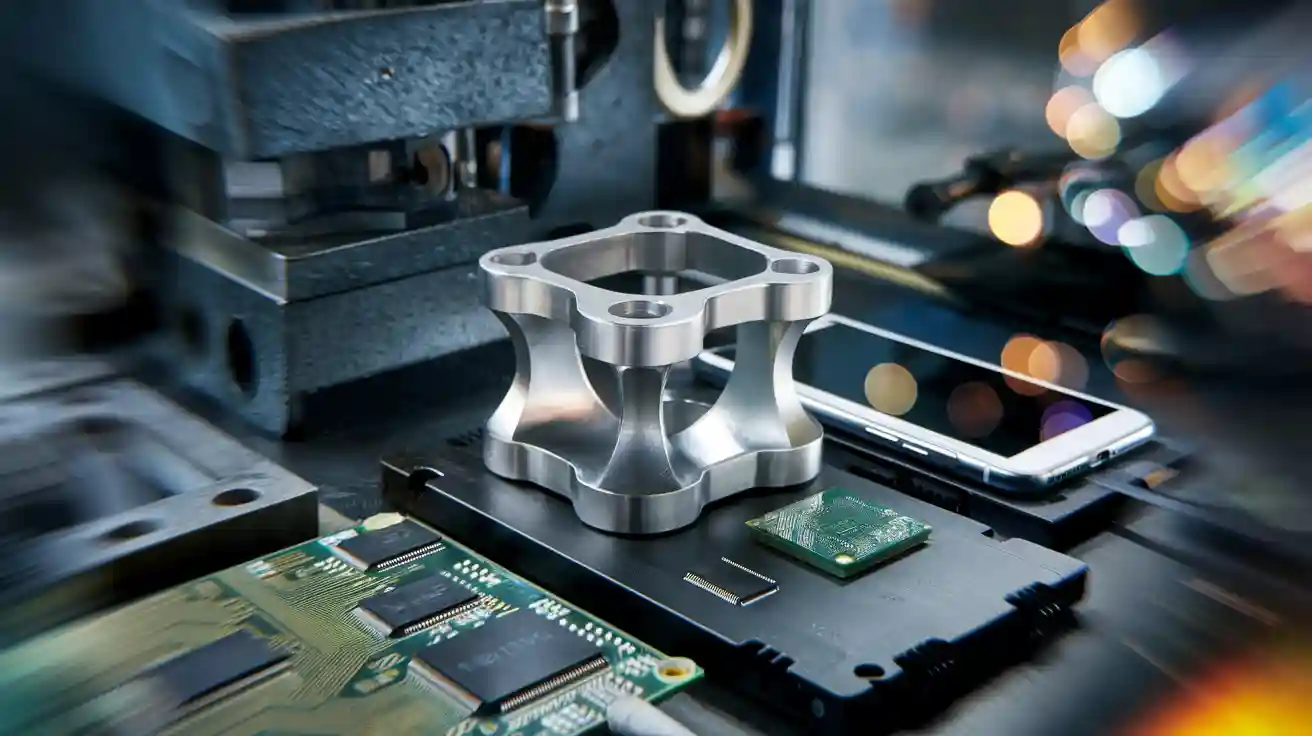

How Aluminum Forging Supports the Electronics Industry
Aluminum forging has become a vital process in the electronics industry. Companies rely on forged aluminum components to achieve lightweight designs, high strength, and precise shapes. Manufacturers choose aluminum forging because it creates parts with excellent surface quality and dimensional accuracy. The electronics sector demands rapid innovation and strict quality, and forging meets these needs by supporting complex designs and reliable performance.
Compared to die casting and pure CNC machining, aluminum forging delivers a superior strength-to-weight ratio, greater corrosion resistance, and enhanced durability, all critical for modern electronic products.
Aluminum Forging in Consumer Electronics
Key Applications
Aluminum forging plays a crucial role in the design and production of modern consumer electronics. Manufacturers use this process to create strong, lightweight, and precise components that meet the high standards of today’s devices. The demand for thinner, more portable, and durable products continues to grow. Aluminum forging applications address these needs by providing parts that combine strength with low weight.
Some of the most common uses of aluminum forging in consumer electronics include:
Smartphone and tablet frames: These parts require high strength and rigidity to protect delicate internal components. Aluminum forging ensures a dense structure and excellent surface finish.
Laptop hinges and bases: Forged aluminum alloys provide the necessary durability and precision for moving parts, supporting repeated opening and closing without wear.
Wearable device shells: Smartwatches and fitness trackers benefit from lightweight forged aluminum, which enhances comfort and portability.
Audio device panels and enclosures: Forged aluminum reduces vibration and resonance, improving sound quality and device longevity.
Connectors and internal supports: Precision forging allows for tight tolerances, ensuring reliable connections and structural integrity.
Heat sinks and thermal management parts: Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity helps dissipate heat, maintaining optimal performance in compact electronics.
Note: The lightweight nature of forged aluminum enables sleek, portable designs. Devices become easier to carry and handle, while maintaining structural integrity and durability.
Component Types
Consumer electronics rely on a wide range of forged aluminum components. Each type must meet strict requirements for surface quality, strength, and performance. The following table highlights common surface treatments and their standards for forged aluminum parts:
Surface Treatment | Key Properties | Typical Applications | Relevant Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
Anodizing | Corrosion resistance, durability, color options | Casings, decorative trim | ASTM B244, ISO 7599, ASTM B580 |
Powder Coating | Vibrant colors, smooth finish | Casings | ASTM B244 (indirect) |
Electrophoresis (E-coating) | Uniform, thin, corrosion-resistant coating | Small components, connectors, casings | N/A |
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Hard, wear-resistant, decorative finishes | Components, decorative trims | N/A |
Manufacturers select aluminum alloys such as 6061, 7075, and 4032 for their excellent strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. These alloys support the production of:
Frames and brackets for smartphones and tablets
Precision hinges and bases for laptops
Lightweight shells for wearables
Durable panels and heat sinks for audio devices
Connectors and internal support structures
Forged aluminum components in audio devices and connectors must deliver:
High strength and rigidity to reduce vibration and ensure accurate sound reproduction
Dimensional precision for perfect fit and reliable assembly
Wear resistance and durability against impact, moisture, and temperature changes
Excellent heat dissipation to maintain performance
Corrosion resistance for long-lasting reliability
Structural integrity with low weight for easy handling and installation
Aluminum forging and aluminum alloy forging allow for complex shapes and tight tolerances. This capability supports the rapid innovation cycle in consumer electronics. The process also enables integrated features, such as threads and mounting points, which reduce assembly complexity and cost.
Aluminum forging applications in electronics help manufacturers achieve high surface quality, lightweight construction, and superior mechanical properties. These advantages make aluminum forging essential for producing the next generation of consumer electronics.
Process Advantages
Structure and Surface Quality
The aluminum forging process transforms raw aluminum into high-performance components for electronics. Manufacturers follow a series of steps to achieve optimal results:
Raw material preparation begins with melting and refining aluminum into ingots.
Melting and casting create preliminary shapes.
Extrusion forms the aluminum under high temperature and pressure.
Heat treatment relieves stress and improves strength.
Mechanical treatment shapes the part and enhances surface quality.
Surface treatment, such as anodizing, coating, or sandblasting, boosts corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
Quality inspection ensures dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Forging applies intense pressure to aluminum, compressing the material and closing internal voids. This technique eliminates porosity and produces a dense, uniform microstructure. The result is a component with high strength and reliability. Multidirectional forging further refines the grain structure, reducing the risk of cracking and improving mechanical properties. These steps guarantee that aluminum forging delivers parts with excellent surface quality and dimensional accuracy.
Manufacturers rely on aluminum forging to produce components with smooth surfaces and consistent finishes. The process supports advanced surface treatments, such as anodizing, which require a dense and defect-free substrate. Electronics companies benefit from parts that resist corrosion and wear, maintaining their appearance and performance over time.
Tip: High-density aluminum forging parts provide better fatigue resistance and durability, which are essential for consumer electronics that face daily use.
Cost and Efficiency
Aluminum forging offers significant advantages in cost and efficiency for electronics manufacturing. The process enables mass production of complex shapes and tight tolerances. Cold forging uses aluminum’s plasticity to form intricate designs at room temperature, reducing material waste and machining time. Features like holes, fins, and delicate patterns can be created in a single operation, minimizing the need for secondary finishing.
Manufacturers achieve near-net-shape production, which means less aluminum is removed during CNC finishing. This approach saves up to 50% in material and processing time compared to pure CNC machining. The use of precise dies and compressive forces ensures exceptional dimensional accuracy and reproducibility. Electronics companies can produce large volumes of interchangeable parts with consistent quality.
Aluminum forging supports high yield rates and reduces the risk of defects. The process produces smooth surface finishes, which lowers the cost of additional treatments. Companies benefit from lower production costs, shorter lead times, and reliable delivery schedules. These advantages make aluminum forging the preferred choice for consumer electronics, where speed and quality are critical.
Key benefits of aluminum forging for electronics:
High density and no porosity
Excellent surface finish
High yield and reduced cost
Suitable for mass production
Complex shapes and tight tolerances
Enhanced dimensional accuracy
Aluminum forging enables manufacturers to meet the demands of the electronics industry. The process delivers components that combine superior structure, surface quality, and efficiency, supporting innovation and competitiveness.
Aluminum Alloys for Electronics
Alloy Selection
Manufacturers in the electronics industry carefully select aluminum alloys to meet the demanding requirements of modern devices. The choice of alloy directly affects the success of aluminum alloy forging. Popular options include the 5xxx and 6xxx series, such as 5052 and 6061, which offer a balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. MIC-6, although a cast aluminum, finds use in precision electronic components due to its dimensional stability. Each alloy brings unique benefits to aluminum alloy forging, supporting the production of frames, enclosures, and internal supports.
Key criteria for selecting aluminum alloys include:
High strength-to-weight ratio for lightweight yet durable parts
Excellent corrosion resistance from the natural oxide layer
Superior thermal and electrical conductivity for heat management
Good formability and machinability for complex shapes
Recyclability, supporting sustainability goals
The following table summarizes common aluminum alloys used in electronics and their relevance to aluminum alloy forging:
Aluminum Alloy Series | Key Properties | Electronics Use | Forging Application |
|---|---|---|---|
5xxx (e.g., 5052) | High strength, corrosion resistance | Enclosures, portable devices | Suitable for forging |
6xxx (e.g., 6061, 6063) | Machinability, structural strength | Device housings, frames | Used in aluminum alloy forging |
MIC-6 (cast) | Dimensional stability | Precision components | Indirectly related |
7xxx (Al-Zn series) | High strength | Aerospace, limited electronics | Less common in electronics forging |
Performance Benefits
Aluminum alloy forging delivers significant performance advantages for electronic components. Different aluminum alloys provide a range of mechanical and thermal properties. For example, 6061 and 5052 excel in corrosion resistance and strength, making them ideal for device housings and structural parts. The high thermal conductivity of certain aluminum alloys supports efficient heat dissipation in heat sinks and radiators.
Mechanical properties such as tensile strength, ductility, and formability ensure that forged parts withstand daily use and mechanical stress. The natural oxide layer on aluminum alloys protects against corrosion, extending the lifespan of electronic devices. Manufacturers also benefit from the ability to create complex shapes and tight tolerances through aluminum alloy forging, which is essential for modern electronics.
Note: The balance between mechanical strength and thermal conductivity in aluminum alloys allows designers to optimize both durability and performance in electronic products.
Aluminum alloy forging also supports environmental sustainability. The recyclability of aluminum alloys reduces waste and aligns with global green initiatives. By selecting the right aluminum alloys and applying advanced forging techniques, manufacturers achieve high-quality, reliable, and efficient electronic components.
Production of Consumer Electronics Components
Manufacturing Scale
The production of consumer electronics relies on advanced manufacturing capabilities and large-scale equipment. Companies that specialize in aluminum forging often operate multiple forging presses, CNC machines, and surface treatment lines. These facilities can handle high-volume orders and produce a wide range of components for smartphones, laptops, wearables, and audio devices.
Manufacturers maintain strict quality certifications to ensure consistent results. Common certifications include:
ISO 9001:2015 for quality management systems
IATF16949 for automotive and electronics industry standards
AS9100 and NADCAP for specialized processes and safety
These certifications show that the manufacturer follows global standards for quality, safety, and process control. Many companies also serve a global customer base, providing components to leading electronics brands. They offer a one-stop service that includes design, aluminum forging, CNC finishing, and surface treatment.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) engineering review plays a key role in the production of consumer electronics. DFM encourages early collaboration between engineers and customers. This process helps optimize designs, reduce unnecessary complexity, and improve manufacturability. Simulation tools and clear communication ensure that each part meets both design and production requirements.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is essential in the production of consumer electronics. Manufacturers use a series of steps to guarantee that every aluminum forging meets strict standards. The process begins with careful material selection and continues through die design, forging, heat treatment, and final inspection.
Key quality assurance steps include:
Statistical Process Control (SPC) to monitor temperature, pressure, and deformation during forging.
Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic and eddy-current testing, to detect internal and surface defects.
Strict control of heat treatment and mechanical processing to achieve the required mechanical properties.
Surface finishing processes like anodizing and powder coating to enhance corrosion resistance and durability.
These steps ensure that each component has the right strength, appearance, and reliability for use in consumer electronics. Companies also use computer-aided design and finite element analysis to create precise molds and dies. This approach supports the high standards required for the production of consumer electronics and helps maintain a competitive edge in the global market.
Impact on End Products
Durability and Reliability
Aluminum forging brings significant improvements to the durability and reliability of consumer electronics. The forging process refines the grain structure of aluminum, making each part tougher and more resistant to wear. This method aligns and elongates the grains, which reduces weaknesses and increases fatigue resistance. As a result, forged aluminum components show higher tensile strength and better dimensional accuracy than cast parts. These qualities make forged aluminum ideal for high-stress applications in electronics, such as hinges, frames, and internal supports.
Manufacturers benefit from the increased durability of forged aluminum. Devices built with these components resist impacts, high temperatures, and daily wear. The dense, uniform microstructure eliminates internal defects, which leads to a longer lifespan for electronic products. Consumers experience fewer breakages and less wear, which means fewer returns and higher satisfaction. The impact on production is clear: companies can deliver reliable products that maintain performance over time.
Forging refines grain structure, making parts tougher and more wear-resistant.
Forged aluminum exhibits superior mechanical properties, including higher strength and lower weight.
The process supports lightweight, durable parts essential for consumer electronics.
User Experience
Forged aluminum parts also enhance the user experience in several ways. The material allows for thin, light, and rigid structures, which improve portability and handling. Devices with forged aluminum frames feel premium and cool to the touch, a quality many consumers associate with high-end products. The forging process enables sleek, minimalist designs with sharp lines and smooth finishes, boosting the visual appeal of electronics.
Aluminum’s strength-to-weight ratio means manufacturers can create lighter devices without sacrificing durability. This weight reduction makes devices easier to carry and use. The metal body also helps dissipate heat, which keeps devices comfortable during extended use. Forged aluminum parts resist corrosion, ensuring that products look new for longer periods. These factors combine to create a positive, lasting impression for users.
Aluminum chassis provide a premium feel and improved aesthetics.
Lightweight, rigid structures enhance portability and comfort.
Superior finishes and corrosion resistance ensure lasting appearance and function.
Aluminum forging enables electronics manufacturers to deliver lightweight, high-precision, and durable products that meet modern demands. Companies benefit from advanced manufacturing techniques, which improve product consistency, reduce defects, and support eco-friendly goals. Quality management systems ensure reliable, repeatable results in high-volume production.
Innovations in forging technology allow for complex, customized components.
Market trends show rising demand for sustainable, high-performance materials.
Electronics brands can stay competitive by choosing aluminum forging for future projects.
FAQ
What makes aluminum forging better than die casting for electronics?
Aluminum forging creates dense parts with no porosity. Die casting often leaves gas pockets, which weaken the structure. Forged components show higher strength, better surface quality, and improved reliability in electronic devices.
Tip: Forged aluminum parts achieve a 99% surface treatment yield.
Which aluminum alloys work best for consumer electronics?
Manufacturers prefer alloys like 6061, 7075, and 4032. These alloys offer excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties. They support high-precision forging and advanced surface treatments.
Alloy | Strength | Corrosion Resistance | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
6061 | High | Excellent | Frames, hinges |
7075 | Very High | Good | Wearable shells |
4032 | High | Good | Connectors, panels |
How does aluminum forging help with heat management in electronics?
Aluminum forging produces parts with high thermal conductivity. Heat sinks and thermal management components made from forged aluminum dissipate heat quickly. This keeps devices cool and maintains stable performance.
What certifications should a reliable aluminum forging supplier have?
A reliable supplier holds certifications like ISO9001 and IATF16949. These standards ensure strict quality control, consistent production, and global compatibility for electronic components.
Note: Certified suppliers deliver parts that meet international electronics industry requirements.

