CNC Machining vs Forging for Motorcycle Aluminum Parts: Which is Better?

Choosing between CNC Machining and forging for motorcycle aluminum parts depends on key differences in priorities. CNC Machining delivers high-quality precision, making it ideal for complex shapes and tight tolerances. Forging provides increased strength for parts that face heavy stress. Those who value customization and superior surface finish may prefer CNC Machining, especially when working with popular aluminum alloys like 6061-T6 and 7075-T6. Cost and production volume also influence the best method for each application.
Key Differences
When comparing motorcycle aluminum parts, the key differences between cnc machining and forging stand out in several important areas. Both processes shape metal, but they do so in unique ways that affect the final part’s strength, precision, and cost.
CNC Machining Overview
CNC machining uses computer-controlled tools to cut and shape aluminum parts from solid blocks. This process allows for high accuracy and the creation of complex shapes. Manufacturers often choose cnc machining for motorcycle parts that require tight tolerances or intricate designs. The process does not change the internal structure of the aluminum, so the strength of the finished part depends on the original material. CNC machining works well with many materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
Forging Overview
Forging shapes aluminum by applying heat and pressure, forcing the metal into a die. This process improves the mechanical properties of the part, making it stronger and tougher. Forged motorcycle parts often handle heavy stress better than machined parts. However, forging usually produces simpler shapes and may need extra finishing steps for detailed features. Forging is most common with metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium.
Tip: For high-volume production, forging often proves more cost-effective due to efficient material use and faster cycle times.
The table below highlights the key differences between cnc machining and forging for motorcycle aluminum parts:
Aspect | CNC مشینی | جعل |
|---|---|---|
Material Properties | High accuracy; strength depends on raw material | Stronger, tougher parts due to improved structure |
Precision and Complexity | Complex shapes, close tolerances | Simpler shapes, may need extra finishing |
Production Efficiency | Costly for high volumes, longer machining times | Efficient for large runs, less waste |
Material Compatibility | Metals, plastics, composites | Mainly metals (aluminum, steel, titanium) |
Understanding these key differences helps motorcycle builders and enthusiasts select the best process for their specific needs.
Forging vs Machining: Strength

Forged Aluminum Strength
Forging vs machining often centers on the question of strength, especially for motorcycle aluminum parts. Forging creates components that excel in high-stress environments. The process uses heat and pressure to deform aluminum, which realigns and refines the grain structure. This transformation leads to a denser and more uniform internal structure. As a result, forged aluminum parts show remarkable mechanical properties.
Forged aluminum endures dynamic loads without failure, making it a top choice for motorcycle parts exposed to constant vibration and impact.
The forging process produces a uniform grain structure, which boosts fatigue resistance compared to cnc machining.
Forged components withstand repeated cycles of stress and strain, which is essential for high-load motorcycle applications.
The refined grain structure from forging increases both tensile and fatigue strength, allowing these parts to handle heavy loads effectively.
The deformation during forging leads to a fine-grained microstructure. This structure reduces the risk of cracks under cyclic stress, which is common in motorcycle use. Forged aluminum also offers improved ductility and toughness. These qualities make forged parts less likely to fracture or deform under extreme conditions. The forging machining process results in fewer defects, which further enhances the reliability of the final product.
Motorcycle manufacturers often select forging when strength and durability are the top priorities. The superior mechanical properties of forged aluminum ensure that critical parts, such as wheels, connecting rods, and suspension components, perform reliably even under harsh riding conditions.
CNC Machined Aluminum Strength
CNC machining produces aluminum parts with high precision, but the process does not alter the internal grain structure of the material. The strength of cnc machined parts depends largely on the properties of the original aluminum stock. Unlike forging, machining removes material to achieve the desired shape, which can sometimes introduce stress concentrations or surface imperfections.
Key Findings | Description |
|---|---|
Surface Finish | The poor surface finish of the as-cast alloy is primarily due to material smearing at lower feed rates. |
Microstructure Impact | The microstructure significantly contributes to the deterioration of surface finish, especially in as-cast alloys. |
Mechanical Properties | The as-cast AlSi10Mg has lower microhardness and yield strength compared to printed materials, indicating that machining processes can affect strength. |
Machined aluminum parts may not match the fatigue resistance of forged components. The forging vs machining debate often highlights this difference. Machined parts can develop micro-cracks or surface flaws during the cutting process. These imperfections may reduce the part’s ability to withstand repeated stress cycles. For motorcycle applications where strength is critical, such as in load-bearing or safety-related parts, forging machining offers a clear advantage.
However, cnc machining remains valuable for parts that require complex shapes or tight tolerances. When strength is less critical, and precision is the main concern, machining provides a practical solution. Motorcycle builders must weigh the benefits of forging vs machining based on the intended use of each component.
CNC Machining: Precision & Customization

Accuracy and Tolerances
CNC machining stands out for its precision and ability to achieve close tolerances. Manufacturers rely on this process when they need motorcycle aluminum parts with exact dimensions. CNC machining uses computer-controlled equipment to maintain accuracy throughout production. This method consistently delivers parts that fit perfectly and function reliably.
The tolerances achievable with CNC machining for aluminum parts are impressive. Standard machining can reach tolerances of ±0.005″ (0.13 mm), while precision machining can achieve even tighter tolerances of ±0.002″ (0.051 mm). The table below shows typical tolerances for motorcycle aluminum components:
Tolerance Type | Tolerance |
|---|---|
Standard Machining | |
Precision Machining | ±0.002 in. (0.051 mm) |
These close tolerances ensure that each part meets strict specifications. Motorcycle builders choose CNC machining when accuracy and precision are essential for safety and performance. The process minimizes errors and reduces the need for manual adjustments.
Customization Potential
CNC machining offers unmatched customization potential for motorcycle aluminum parts. This process allows manufacturers to create intricate designs and complex geometries that forging cannot match. CNC machining supports high design flexibility, enabling builders to produce unique parts tailored to specific needs.
The table below highlights the advantages of CNC machining compared to forging:
Advantage | CNC مشینی | جعل |
|---|---|---|
Precision | Limited precision | |
Complexity | Capable of intricate geometries | Simpler shapes |
Design Flexibility | High design flexibility for customization | Less flexible in design |
Surface Finish | Superior surface finishes | Basic surface finishes |
Material Efficiency | Optimizes material removal | Minimizes waste but less precise |
Motorcycle enthusiasts often select CNC machining for custom projects. The process enables the creation of personalized components, such as unique brackets, levers, or decorative covers. CNC machining also produces superior surface finishes, which enhance both appearance and performance. The ability to combine precision, accuracy, and customization makes CNC machining the preferred choice for builders who demand excellence.
Production Efficiency & Cost
Low vs High Volume
Manufacturing motorcycle aluminum parts involves important decisions about production volume. CNC machining works best for low to medium production runs. The process allows for quick changes in design and supports tight tolerances, making it ideal for custom or limited-edition parts. Machined parts can be produced in small batches without high upfront costs. However, as the batch size increases, the cost per part drops because the fixed costs of programming and setup spread over more units. This effect, known as economies of scale, makes CNC machining more cost-effective for larger runs. In contrast, forging becomes more efficient as production volume rises. The initial investment in dies and equipment is high, but the per-part cost decreases sharply with higher quantities. Forging suits mass production where mechanical strength and consistency matter most.
Tip: For custom or prototype motorcycle parts, CNC machining offers flexibility and precision. For large-scale manufacturing, forging delivers better value and strength.
Lead Time & Sourcing
Production speed and sourcing of raw materials play a major role in manufacturing efficiency. Lead times for aluminum parts usually range from 1 to 4 weeks, depending on order size and complexity. CNC machined parts can be delivered in as little as 5 days for simple designs. More complex machined parts may require several weeks. Forged parts often take longer due to the need for die creation and post-processing.
The sourcing of aluminum alloys affects both machining and forging timelines. The table below outlines the main steps in sourcing and preparing aluminum for manufacturing:
Step | Description | Impact on Production Speed |
|---|---|---|
Bauxite Mining | Extraction of bauxite ore, the primary source of aluminum. | Sets the stage for all subsequent processes. |
Bayer Process | Refining bauxite to obtain alumina. | Influences purity and machining efficiency. |
Smelting | Converting alumina to aluminum metal through electrolysis. | Impacts mechanical strength and machining speed. |
Casting | Pouring molten aluminum into molds to create shapes. | Affects part complexity and machining time. |
Rolling/Extrusion | Shaping aluminum into sheets or profiles. | Directly impacts machinability and speed. |
Heat Treatment | Enhancing material properties through controlled heating and cooling. | Improves strength and tight tolerances. |
Manufacturers choose the process that matches their needs for mechanical strength, tight tolerances, and production speed. CNC machining provides rapid turnaround for machined parts, especially when using readily available aluminum alloys. Forging requires more preparation but excels in high-volume manufacturing where mechanical strength is critical.
Material Compatibility
Aluminum Alloys for CNC
CNC machining supports a wide range of aluminum alloys. Each alloy offers unique properties that suit different motorcycle parts. Manufacturers select alloys based on machinability, strength, and the specific requirements of the part. The table below highlights common aluminum alloys used in CNC machining for motorcycle applications:
Aluminum Alloy | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
6061-T6 | Versatile, easy to machine, good strength-to-weight ratio | Automotive parts, bicycle frames, computer parts |
7075-T6 | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio, hardness comparable to softer steels | High-stress applications in aerospace, military, high-performance bikes |
2024-T4 | Moderate- to high-strength, good fatigue resistance | Aerospace applications |
MIC 6 | High machinability, excellent accuracy, stress-relieving properties | High-tolerance plates |
6082 | Higher tensile strength than 6061, corrosion-resistant | Various applications requiring high strength |
6061-T6 remains a popular choice for motorcycle parts due to its balance of strength and machinability. 7075-T6 provides higher strength, making it suitable for performance-focused components. MIC 6 excels in applications that demand tight tolerances and stability. Each alloy allows CNC machining to deliver precise and reliable parts.
Aluminum Alloys for Forging
Forging uses specific aluminum alloys that respond well to heat and pressure. These alloys must combine strength, ductility, and resistance to corrosion. The table below lists common alloys used in forging for motorcycle parts:
Alloy Type | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
A356.0 | Good castability, strength, ductility, corrosion resistance | Wheel hubs |
6061 | Excellent corrosion resistance, weldability, good strength | Various applications, including wheel hubs |
7075 | High strength, good fatigue strength | Performance-oriented applications |
2024 | High strength, good fatigue resistance | Aerospace and high-strength applications |
Alloys like 6061 and 7075 offer a strong combination of durability and fatigue resistance. A356.0 stands out for its castability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for wheel hubs. Forging with these alloys produces parts that maintain low density and moderate strength. These alloys also provide corrosion resistance and easy shaping, which help manufacturers create durable and recyclable motorcycle components.
Note: Choosing the right alloy for forging ensures the final part meets the demands of both performance and longevity.
Surface Finish
CNC Surface Quality
CNC machining produces a superior surface finish for motorcycle aluminum parts. The process uses precise cutting tools that create smooth and consistent surfaces. Manufacturers can control the surface finish by adjusting tool speed, feed rate, and cutting parameters. This control allows them to achieve a range of surface roughness values, which suit different applications.
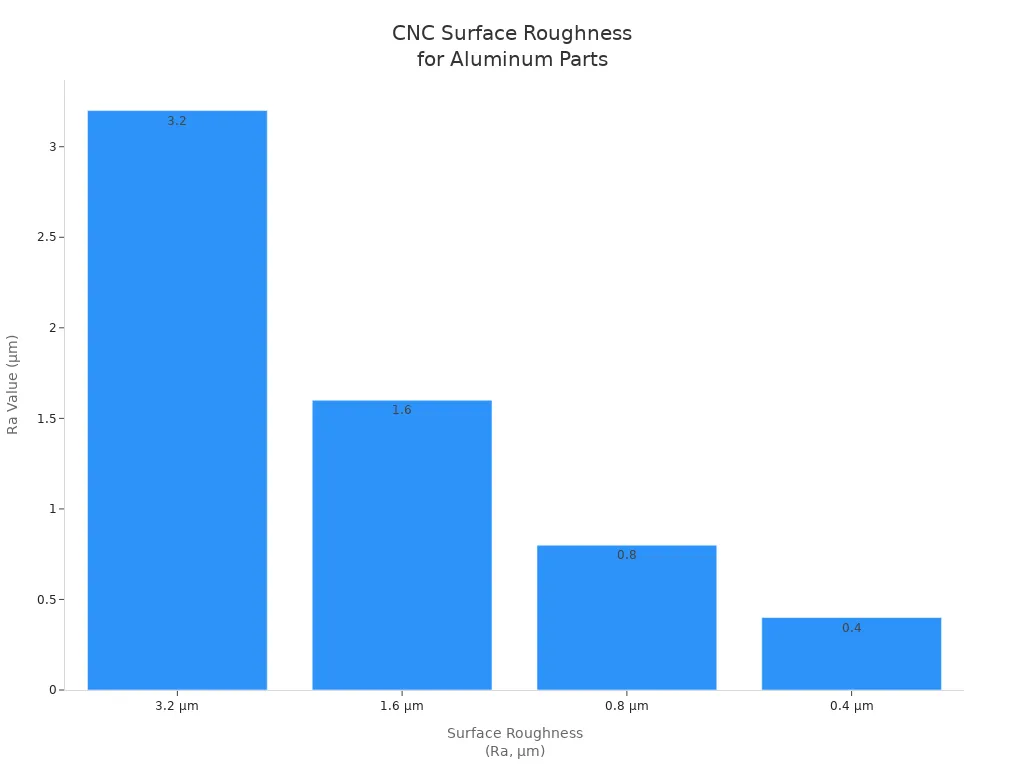
The table below shows typical surface roughness values for CNC machined aluminum parts:
Surface Roughness (Ra) | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
3.2 µm | Suitable for structural parts that do not require a polished finish. | Machine brackets, automotive engine covers, general tooling fixtures, machine chassis. |
1.6 µm | Recommended for tight fits and parts under stress. | Parts subject to moderate stress and vibrations. |
0.8 µm | High-grade finish for parts under stress concentration. | Suitable for vibrating and moving components. |
0.4 µm | Very high-grade smooth texture, often polished. | Ideal for rapidly moving or vibrating parts under high tension. |
CNC machining can achieve a mirror-like surface finish, which appeals to riders who want both performance and aesthetics. Machined aluminum is easy to polish, making it ideal for those seeking shiny components. The process also supports anodizing, which adds color and further improves the surface finish. Many motorcycle builders choose CNC machining when they need a high-quality surface finish for custom or visible parts.
Forging Surface Quality
Forged aluminum parts display a different surface finish compared to CNC machined components. The forging process creates a work-hardened surface, which increases strength but often results in a rougher texture. The initial surface finish from forging may show marks from the die and require additional steps to improve appearance.
Forged parts have a work-hardened surface and aligned grain structure, which enhances strength.
The surface finish of forged parts is less visually appealing without extra finishing.
Many manufacturers use abrasive blasting or polishing to improve the surface finish of forged parts.
The table below compares the surface finish and related features of forged and CNC machined parts:
Feature | Forged Parts | CNC Machined Parts |
|---|---|---|
Surface Finish | Work-hardened, may require abrasive blasting | High level of craftsmanship, mirror-like finish |
Strength | Superior due to aligned grain structure | Generally lower than forged parts |
Aesthetic Appeal | Less visually appealing without finishing | Highly reflective, visually appealing |
Forged parts may not match the surface finish of CNC machined parts right out of the process. However, with post-processing, the surface finish can improve significantly. Motorcycle manufacturers often select forging for parts where strength matters more than appearance. When a high-quality surface finish is essential, CNC machining remains the preferred choice.
Choosing the Right Process
When to Choose CNC
CNC machining fits projects that demand high precision and complex shapes. Motorcycle builders often select this process for custom parts or prototypes. CNC machining allows for tight tolerances, which ensures each component fits perfectly. The process supports a wide range of aluminum alloys, making it versatile for different applications.
Motorcycle enthusiasts value CNC machining for its ability to create unique designs. The process enables intricate details, such as custom logos or lightweight cutouts. CNC machining also produces a superior surface finish, which appeals to those who want visually striking parts. Small production runs benefit from CNC machining because setup costs remain low and design changes are easy to implement.
A table below summarizes when CNC machining is the preferred choice:
Scenario | Why CNC Machining Excels |
|---|---|
Custom or prototype parts | High flexibility and quick changes |
Complex geometries | Precise cutting and shaping |
Tight tolerances | Consistent accuracy |
Superior surface finish needed | Smooth, polished results |
Tip: CNC machining is optimal for your project when customization, accuracy, and finish matter most.
When to Choose Forging
Forging stands out for motorcycle parts that require maximum strength and durability. The process changes the grain structure of aluminum, which improves mechanical properties. Forged parts handle high stress and repeated impacts better than machined parts.
Motorcycle manufacturers often choose forging for critical components. These include wheels, connecting rods, and suspension arms. Forged aluminum parts also offer several additional benefits:
Improved strength from refined grain structure, making them ideal for high-stress applications.
Lighter weight allows for thinner designs without sacrificing durability, which enhances motorcycle performance.
Better resistance to corrosion increases the lifespan of parts exposed to harsh environments.
Forging becomes cost-effective for large production runs. The initial investment in dies pays off when producing many identical parts. Builders who prioritize strength and longevity often select forging for essential motorcycle components.
Motorcycle builders should match the process to their priorities. Forging delivers outstanding durability and low maintenance, making it ideal for high-stress parts. CNC machining excels in precision and customization, often leading to higher customer satisfaction.
Many customers prefer CNC machined parts for their perceived quality and appearance.
Common mistakes in CNC machining include incorrect tool selection, poor setup, and neglecting maintenance. Careful planning helps avoid these issues. Riders should weigh strength, cost, and design needs before choosing the best method for their project.
FAQ
What makes forged parts stronger than CNC machined parts?
Forged parts gain extra strength and sturdiness because the forging process realigns the grain structure. This change improves toughness and mechanical characteristics. Motorcycle builders choose forged parts for high-stress areas that need strong and durable parts.
Can CNC machining create complex shapes for motorcycle aluminum parts?
CNC machining produces complex shapes with high precision. The process uses computer-controlled tools to cut aluminum into high-quality components. Builders select CNC machining when they need unique designs or intricate details that forging cannot achieve.
Are forged parts always better for toughness?
Forged parts offer superior toughness due to their refined grain structure. This property helps them resist cracks and fatigue. However, CNC machined parts can also provide toughness when made from high-quality components and suitable alloys.
Do forged parts require extra finishing for a smooth surface?
Forged parts often need additional finishing steps, such as polishing or blasting, to achieve a smooth surface. The initial texture from forging may show die marks. CNC machining delivers smoother surfaces without much post-processing.
Which process is more cost-effective for producing strong and durable parts in large quantities?
Forging becomes more cost-effective for large production runs. The process creates strong and durable parts with consistent mechanical characteristics. CNC machining suits smaller batches or parts with complex shapes, but forging excels in mass production.

