
What is Forging
Forging changes metal by pressing, hammering, or rolling it with strong force. This keeps the metal solid and makes it much stronger than other ways to shape metal. Many companies use forging to make parts that must hold heavy weight or be used a lot. Forging lines up the grain structure in the metal. This makes the metal stronger and helps it last longer. The table below shows how forging is different from other ways to make metal parts:
Attribute | Billet Steel | Forged Steel |
|---|---|---|
Strength | Moderate | High |
Grain Structure | Less uniform | Uniform |
Fatigue Resistance | Moderate | High |
Forging is important because it helps make things like car engine parts, industrial tools, and airplane parts stronger and more dependable.
Forging Process
How Forging Works
The forging process shapes metal by using strong force while the metal stays solid. People use this method to make parts that need to be tough and reliable. The steps to the forging process help change the metal’s structure and improve its strength.
Here are the main steps to the forging process:
Heat the metal to the right temperature. For hot forging, the metal often glows bright orange or red, which means it is above 1500°F. Cold forging skips this step and works at room temperature.
Place the metal between special tools called dies or rolls. The type of die or roll depends on the forging process being used.
Apply compressive forces with hammers, presses, or rolls. These tools push and squeeze the metal into the desired shape.
For some forging operations, like closed-die forging, the process uses several stages. The first stage shapes the rough outline, the next stage forms the basic shape, and the final stage adds details.
In roll forging, the metal passes between shaped rolls. This step stretches and thins the metal bar.
Remove any extra material, called flash, if it forms during the process.
Note: The forging process does not melt the metal. It keeps the metal solid, unlike casting, which pours liquid metal into a mold.
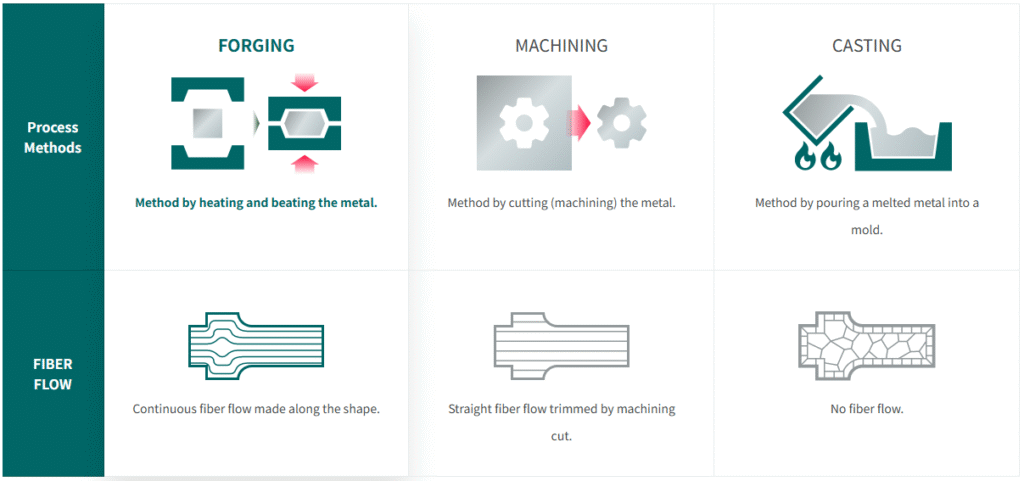
Forging stands out from other metalworking methods because it changes the grain structure inside the metal. The steps to the forging process align the grains in a certain direction, making the part stronger and more resistant to wear. This is different from casting, where the metal cools from a liquid and the grain structure forms randomly.
Compressive Forces in Forging
Compressive forces play a key role in the forging process. These forces press and squeeze the metal, causing it to flow and fill the shape of the die or roll. The steps to the forging process use these forces to change the metal’s microstructure.
When the forging process applies compressive forces, the grains inside the metal become smaller and line up in the direction of the force. This grain refinement makes the metal harder and stronger. The forging process also increases the number of dislocations, or tiny shifts, in the metal’s structure. These changes boost the metal’s strength and toughness.
Forged parts have a grain structure that follows the shape of the part. This gives them better mechanical properties than parts made by other methods. Forging reduces defects like air pockets or weak spots, which can happen in casting. The forging process also uses less energy than some other metalworking methods, such as machining, because it does not remove much material.
Tip: Forging creates parts with high strength, good wear resistance, and fewer defects. This makes forged parts ideal for demanding uses in cars, airplanes, and heavy machinery.
Types of Forging Processes
Forging shapes metal in different ways to make strong parts. The main types are open-die forging, closed-die forging, seamless rolled ring forging, hot forging, and cold forging. Each type has its own steps and works best for certain things.
Open-Die Forging
Open-die forging uses flat or simple dies to shape metal. The metal is not fully covered, so workers move and turn it to get the right shape. This method is good for big or simple items like shafts, cylinders, and discs. Car and airplane companies use open-die forging for strong, reliable parts. It can handle very large pieces, even over 100 tons.
Open-die forging helps the grain flow better and makes parts stronger. It saves money for small or medium amounts of parts.
Closed-Die Forging
Closed-die forging, or impression-die forging, presses metal into a shaped die. The metal fills the space and makes detailed, exact parts. This way is great for making many of the same part fast. Closed-die forging makes things like gears, rods, and tools. It is more exact than open-die forging and often needs less work after.
Aspect | Open-Die Forging | Closed-Die Forging |
|---|---|---|
Lower; needs more machining | Higher; less machining needed | |
Production Volume | Low to medium | High |
Seamless Rolled Ring Forging
Seamless rolled ring forging makes strong rings by rolling a pierced metal piece into a circle. The grain in the ring follows its round shape, which makes it very strong. These rings are used in jet engines, turbines, and gearboxes. This method is good for parts that face a lot of stress, pressure, or heat.
Rings made this way are lighter and stronger than cast or welded rings.
They last longer and do not wear out fast, which keeps things safe.
Cold and Hot Forging
Hot forging heats metal until it is very hot, so it is easier to shape. This makes the metal bend better and take hits without breaking. Hot forging is used for hard shapes and tough metals. Cold forging shapes metal at room temperature. It makes the metal harder and stronger but can also make it break easier. Cold forging is best for simple shapes and making lots of parts like bolts and screws.
Aspect | Hot Forging | Cold Forging |
|---|---|---|
Temperature | High | Room temperature |
Strength | Good ductility, less hardness | High strength, more hardness |
Surface Finish | May need polishing | Smoother finish |
Typical Uses | Complex, tough parts | Simple, mass-produced parts |
Different Types of Forging
Manufacturers pick the forging type based on the part’s size, shape, and job. Open-die forging is good for big, simple parts. Closed-die forging is better for small, detailed items. Seamless rolled ring forging is best for rings that must handle stress. Hot and cold forging let companies choose how strong or hard the part is and how fast they can make it. Knowing the types of forging helps companies choose the best way for each part.
Forging vs. Other Methods
Forging vs. Casting
Forging and casting both shape metal, but they do it differently. Forging keeps the metal solid while shaping it. Casting melts the metal and pours it into a mold. These ways make parts with different strengths. Forging uses strong force to press or hammer the metal. This lines up the grain inside the metal. Forged parts are stronger and more dependable. Casting can make tricky shapes and big parts. But the grain inside is not as even. This can cause weak spots or problems in the part.
Here is a table that shows the main differences between forging and casting:
Aspect | جعل | Casting |
|---|---|---|
Mechanical Strength | Superior strength, toughness, fatigue resistance | Lower strength; possible internal defects |
Durability | High durability for high-stress uses | Lower durability; may need extra work |
Grain Structure | Aligned and refined | Less uniform |
Typical Applications | Crankshafts, gears, medical implants | Engine blocks, pump bodies, decorative items |
Limitations | Not for very complex or huge parts | Good for complex shapes and large parts |
Defects | Fewer defects | Possible porosity, cracks, or shrinkage |
Forging vs. Machining
Forging and machining both start with solid metal, but they change it in different ways. Forging heats the metal until it is soft. Then it presses or hammers the metal into shape. This makes the grains inside tighter and stronger. Machining cuts away pieces from a solid block. It does not change the inside of the metal. Machining is good for making detailed shapes. But it does not make the part stronger.
Forged parts have tighter grains and fewer weak spots. This helps them handle heavy loads or stress. Machined parts can be very exact, but they may not be as strong as forged parts.
Cost and Performance Comparison
Forging can cost more at first because it needs special tools and strong machines. But forged parts usually last longer and need fewer repairs. This can save money over time. Casting can be cheaper for big or tricky shapes, but those parts may not be as strong. Machining can waste more metal, which makes it cost more. Forging uses more of the metal, so there is less waste.
Many companies pick forging when they need parts that must not break, like in cars or airplanes. Forged parts work better and are safer.
Applications of Forging in Modern Industries
Forging is very important in today’s industries. Many companies use forging to make parts that must be strong and last a long time. Forged parts are found in things people use every day and in big machines.
Automotive Industry
Car makers use forging to make parts that face stress and wear. They use forged aluminium and steel to make cars lighter and stronger. This helps cars use less fuel and pollute less. Some common forged car parts are:
Shafts and gears for engines and transmissions
Strong aluminium and steel parts for the car’s body
Parts for electric cars and new energy vehicles
Forging lets car makers build parts that last longer and work better.
Aerospace Components
Airplane companies use forging for important airplane parts. Forged airplane parts must handle high pressure, heat, and force. These parts include landing gear, engine parts, and frames. Forging makes these parts strong and safe for flying.
Motorcycles and Bicycles
Motorcycles and bicycles use forged parts to be safer and last longer. Forged metal makes frames, wheels, and rods stronger. Electric motorcycles and bikes also use forged parts for better wear resistance and longer life.
Industrial and Consumer Goods
Many tools and products use forged parts for extra strength. Some examples are:
Cars
Electric motorcycles
Tools and hardware
Forged parts help these products resist wear, rust, and damage. This means they last longer and work well in hard conditions.
Forging helps companies make products that are safe and work well.
Advantages of Forging
Superior Strength and Durability
Forging makes parts that are very strong and tough. The process changes the metal’s grain pattern. This new pattern helps spread force across the part. Forged parts do not get tired or break as easily. They also fight off rust and heat better than cast parts. Forging breaks up bad spots in the metal and spreads them out. This makes the part cleaner inside. Many companies use forged parts for important jobs. For example, landing gear, jet engine shafts, turbines, crankshafts, gears, and hand tools all use forged parts. These parts must hold heavy weight and work in tough places every day.
Forged parts are tougher and last longer.
They work well in hard jobs and rough places.
Many important machines use forged parts to stay safe.
Better Grain Structure
Forging changes the grains inside the metal. The grains line up with the shape of the part. This makes the part stronger and less likely to crack. The even grain pattern helps stop damage. Forged parts often work better than cast or machined parts because of this.
Material Efficiency and Less Waste
Forging uses more of the metal and wastes less. Near net shape forging can use over 90% of the metal. This means most of the metal becomes the finished part. Machining often throws away more than half of the metal. Forging saves metal and lowers costs. Companies save money and use fewer resources with forging.
Enhanced Surface Treatment Compatibility
Forged parts take coatings and heat treatments very well. The tight, even metal helps these treatments stick and last longer. This makes the part better at fighting rust and wear. Forged parts often meet high quality rules. Quality checks in forging look at heat, pressure, and how the metal moves. Inspectors test the strength and hardness of each part. Special tests like ultrasonic or radiographic testing find hidden problems. These steps make sure forged parts are safe and work well.
Forging gives us strong, safe, and efficient parts for today’s industries.
Forging changes metal into strong parts for cars, planes, and tools. These parts help things work well every day. The forging industry is growing fast. New tools like computers and robots help make forging better and faster. Many companies pick forging because it makes tough parts with less waste. Forged parts also work better than some other parts.
Forging gives high strength, lasts long, and can be used in many ways.
Places like the Industrial Forging Knowledge Center teach people about forging and metalworking.
Forging is still very important in making things today. Learning about forging helps people see how things we use are made.
FAQ
What makes forged parts stronger than cast parts?
Forged parts have grains that follow the shape of the part. This grain flow gives the part more strength and toughness. Cast parts have random grain patterns, which can create weak spots.
What materials do manufacturers use for forging?
Manufacturers often use steel, aluminum, titanium, and copper for forging. These metals work well because they can handle high pressure and heat. Each metal gives different properties to the finished part.
What products use forged parts most often?
Many cars, airplanes, bicycles, and tools use forged parts. These products need strong, reliable pieces that can handle stress and wear. Forged parts help these products last longer and work better.
What is the main difference between hot forging and cold forging?
Hot forging and cold forging differ in the materials they can process and the outcomes they achieve. Cold forging is typically used for softer metals, such as 1xxx series aluminum alloys, and allows for higher dimensional accuracy with minimal post-processing. However, it’s limited in shape complexity and deformation volume. In contrast, hot forging is suitable for harder metals and can produce parts with greater strength due to better grain flow. While hot forging enables the forming of more complex shapes, it usually requires additional machining to meet tight tolerances.

